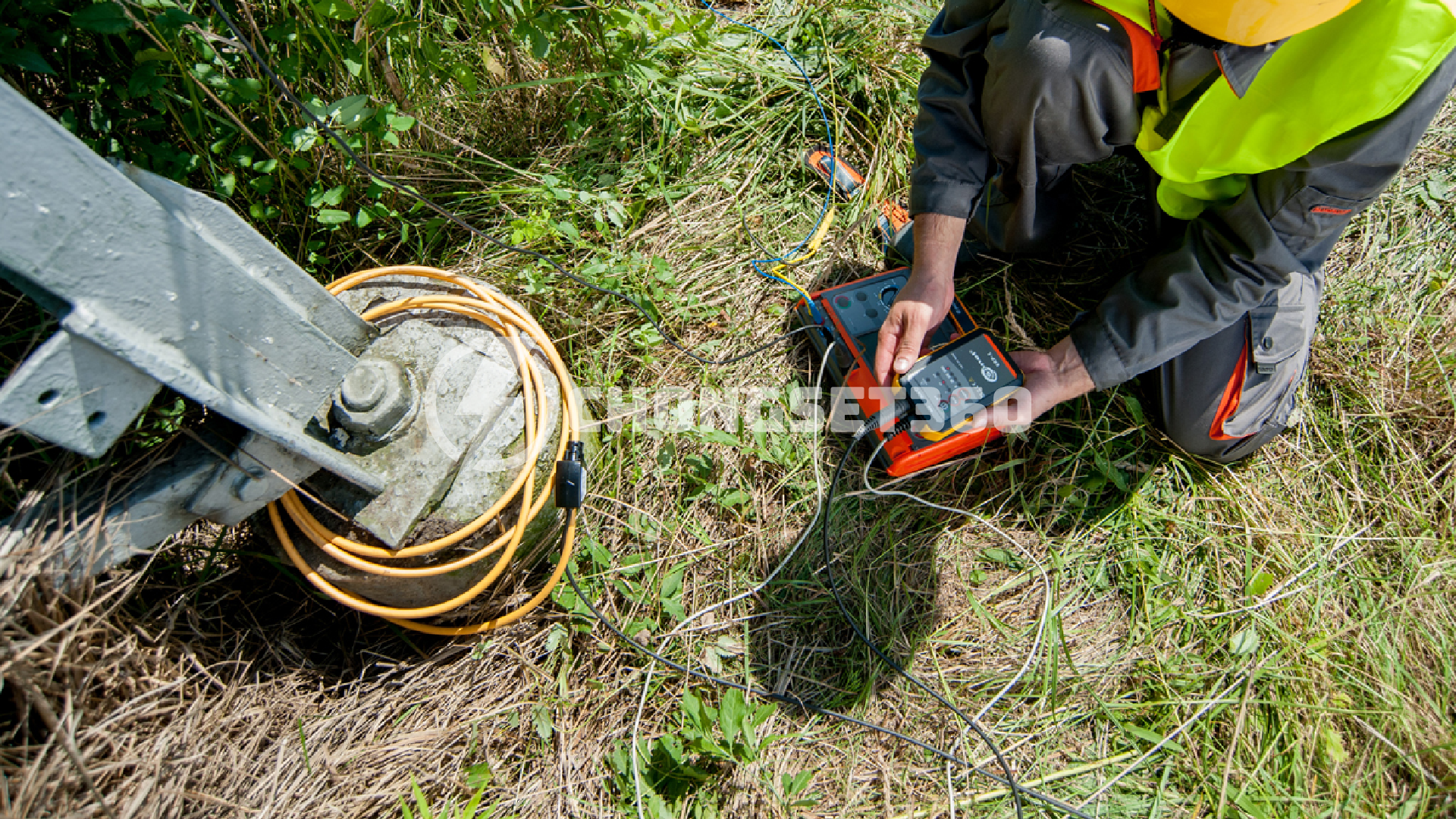
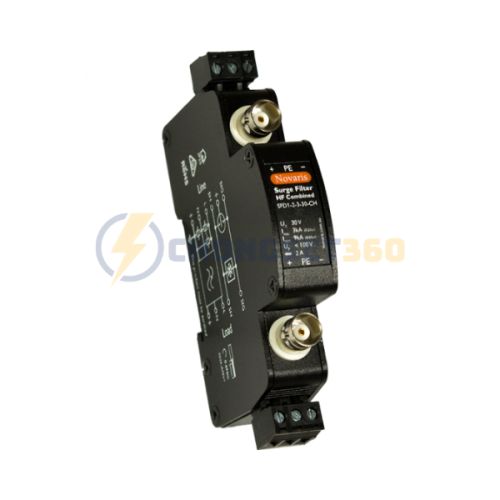
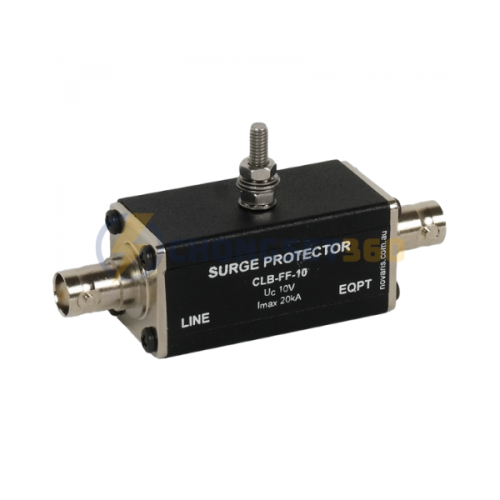
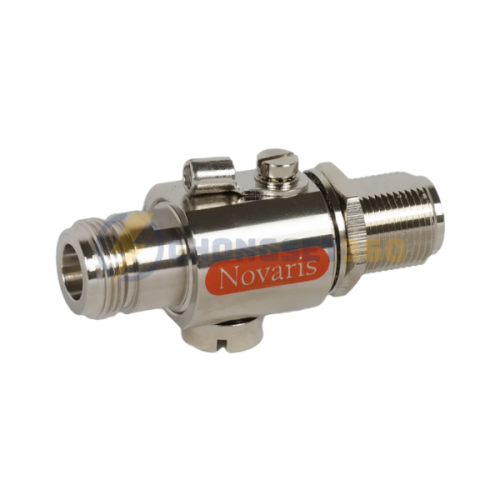
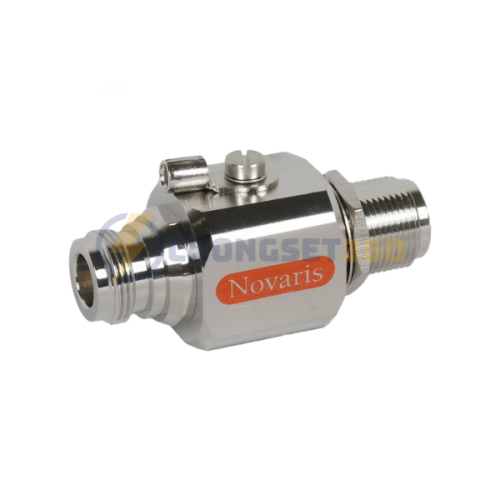
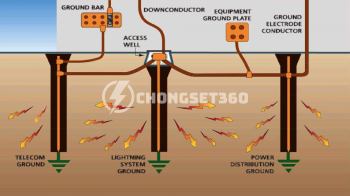
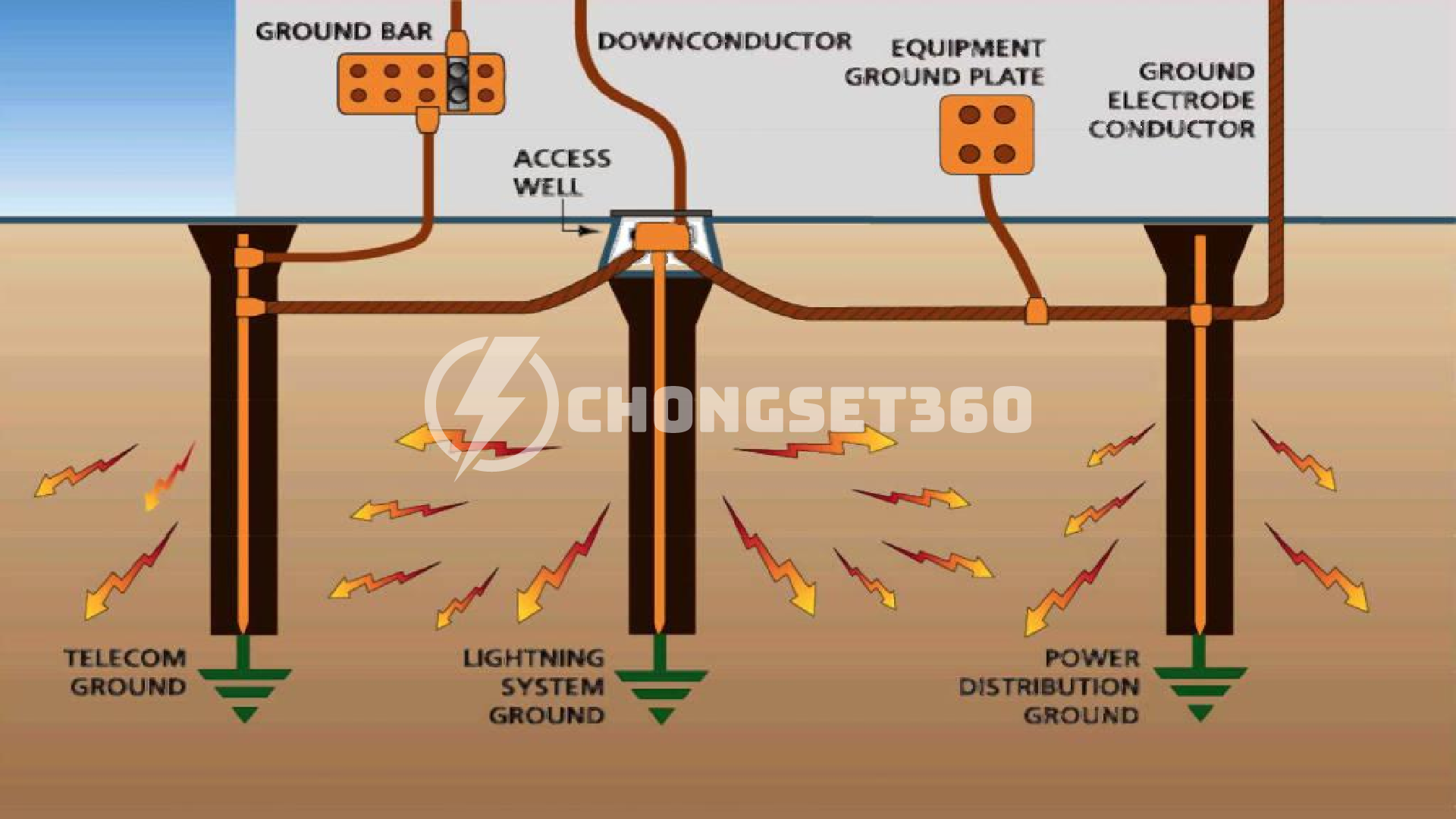
Tầm nhìn
Chúng tôi đang từng bước thực hiện mục tiêu trở thành một trong những đơn vị hàng đầu trong lĩnh vực cung cấp giải pháp. tư vấn, thiết kế & thi công thiết bị chống sét
Sứ mệnh
Sứ mệnh của chúng tôi là đem lại những giải pháp và dịch vụ tốt nhất, chất lượng sản phẩm và uy tín thương hiệu là ưu tiên hàng đầu chúng tôi cam kết mang tới cho khách hàng.